 As a consequence of reclassifying broadband as a utility service to protect Net Neutrality, the FCC may have unintentionally opened the door for a Universal Service Fund surcharge on broadband service.
As a consequence of reclassifying broadband as a utility service to protect Net Neutrality, the FCC may have unintentionally opened the door for a Universal Service Fund surcharge on broadband service.
Telephone customers have been accustomed to paying “USF” fees as part of their monthly phone bill since 1997. The average household pays just under $3 a month into the fund, which subsidizes four key programs:
- Connect America Fund: Originally designed to subsidize telephone service in high cost rural areas, the program has increasingly shifted towards subsidizing broadband expansion in remote areas where private telephone companies won’t expand service without monetary assistance from the fund. In 2013, $4.17 billion was paid in the form of subsidies to mostly rural and independent telephone companies;
- Lifeline: The Lifeline program pays up to $10 a month to a participating telephone or wireless company to subsidize basic telephone service for Americans living below 135% of the poverty line. More than 17 million households take part, most getting basic landline service for around $1 a month;
- Rural Telemedicine: By subsidizing video conferencing and high-speed Internet access, rural doctors can consult with specialists in larger urban areas to help treat rural patients without the cost and risk of transporting the sick or injured to distant hospitals;
- E-Rate: A needs-based subsidy program for schools and libraries seeking telecom services and Internet access. The subsidies help defray the cost of the services on a sliding scale, with rural and urban poor areas getting the largest subsidies.
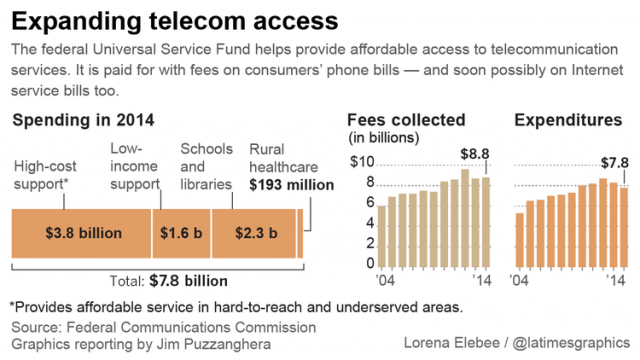 The fund has increasingly shifted towards Internet connectivity and service, but only telephone customers now pay a USF surcharge on their bill.
The fund has increasingly shifted towards Internet connectivity and service, but only telephone customers now pay a USF surcharge on their bill.
Net Neutrality critics warned that reclassifying broadband under Title II as a telecommunications service would open the door for new fees on broadband bills, some predicting as much as $11 billion a year in new fees. But because the FCC caps the amount of the fund each year, FCC chairman Thomas Wheeler predicted even if broadband customers are asked to contribute to the USF fund, the amount would be split between phone and broadband service, resulting in no additional out-of-pocket costs. Under that scenario, a phone customer currently paying $3 a month in USF charges would see that amount reduced to $1.50 a month on their phone bill, with a new $1.50 charge on broadband. The end amount is the same.
At least for now.
The FCC has been gradually increasing the size of the fund over the years, up 47% since 2004. Last year the FCC increased the fund by $1.5 billion to raise $8.8 billion from ratepayers nationwide. Most of the increase went to rural broadband deployment.
Industry-funded Net Neutrality critics are pushing a Los Angeles Times story about the potential for new fees, calling them ‘runaway government spending.’ But in perspective, the FCC’s $8.8 billion dollar effort to improve broadband accessibility is a fraction of the amount spent on highly controversial military projects. The F-35 Lightning II aircraft, for example, will cost taxpayers $1.5 trillion, and the Republican Congress approved $500 billion in extra funding this year for the project, funds above and beyond what the Pentagon requested. If that extra funding was spent on broadband improvements, every home in America could be wired for fiber optic Internet access. For $1.5 trillion, every home in the western hemisphere could be guaranteed broadband.
If USF fees are applied to broadband service, it is safe to expect your provider will pass along the fee as a new line item on your bill.


 Subscribe
Subscribe

 What will happen in Verizon service areas that are not considered priorities?
What will happen in Verizon service areas that are not considered priorities?
 Alaska’s largest cable company today unveiled changes to its Internet plans, ditching surprise overlimit fees in favor of a speed throttle.
Alaska’s largest cable company today unveiled changes to its Internet plans, ditching surprise overlimit fees in favor of a speed throttle.

