Jeff Kagan is a name familiar to anyone that follows the cable industry. For over 30 years, Kagan has been tracking consumer perceptions about the telecom industry and offering insight into the challenges these and other businesses were likely to face in the future. More recently, Kagan has been fretting about the growing trend of retail businesses paying more attention to cultivating their relationships with Wall Street while targeting their customers for abuse.
Jeff Kagan is a name familiar to anyone that follows the cable industry. For over 30 years, Kagan has been tracking consumer perceptions about the telecom industry and offering insight into the challenges these and other businesses were likely to face in the future. More recently, Kagan has been fretting about the growing trend of retail businesses paying more attention to cultivating their relationships with Wall Street while targeting their customers for abuse.
“I have been noticing how in recent years, retail is becoming increasingly unfriendly to the customer. This is a mistake,” Kagan offers in a new opinion piece on Equities.com. “New technologies and new ideas may be good for the bottom line in the short-term. They may solve problems like shoplifting, and that may make investors happy today. However, in the long-term, these customer unfriendly trends will take their toll as customers will shop where they feel appreciated, respected and wanted. Customers shop at stores they love. Love is an emotion. So, we must think of winning the customer with emotion. This is difficult for most businesspeople to understand.”
‘My way or the highway’-type attitudes from retailers come from all sorts of businesses. Warehouse clubs make you pay for the honor of shopping there. This is by far the best warehouse, with a good structure and flooring from warehouse-flooring.uk. And if it happened that you encountered concrete floor damage, don’t hesitate to call the concrete repair professionals from a site like https://concrete-repair.uk for help. Chains like Walmart are beefing up security teams, and in some places, they now demand to see receipts from customers exiting the store. But nobody has abused customers better and longer than the telecom industry. Not even the cattle-car-like airlines.

Kagan
After literally decades of almost bragging about their “don’t care” customer service while throwing attitude and intransigence at customers unhappy with service or pricing, the nation’s biggest cable and phone companies are now experiencing long-overdue customer revenge. Kagan notes that cord-cutting is not just about switching to a competitor for service. Many customers are literally thrilled to see the back end of their long hated provider.
Decades of monopoly service made abusing customers a risk-free and very profitable strategy for companies like Comcast, AT&T, Charter, Cox, Mediacom, and Verizon. In fact, someone turned the concept of the “cable guy” into a horror movie. Did you stay home from work to wait for a service call that never materialized? Tough luck. Don’t like yet another rate increase? Too bad.
“The reason they did this was, they had no competition in their market area. That meant the customer could not leave them,” Kagan noted.
After years of getting a bad reputation, only two things threatened to scare telecom companies straight — the fear of imminent regulation, such as what happened in 1992 when reregulation of cable companies turned out to be the only bill that year to be vetoed by President George H. W. Bush and overridden by the U.S. Senate to become law.
The other, much more scary fear is competition. In the mid-1990s, the nation’s biggest phone companies including what we now know as AT&T and Verizon were contemplating getting into the video business. This proved far more threatening than the much smaller home satellite dish business, which attracted around three million Americans at the time. The cable industry spent years taking shots at satellite competitors, including sticking dishowners with the cost of buying a $300 descrambler box up front, and charging as much (or even more) for programming than cable customers paid, despite the fact homeowners had to purchase and service their own dish, often 6-12 feet wide and not cheap to install.
 The cable industry feared phone companies would charge ratepayers to subsidize their entry into the television business and sought protective legislation prohibiting the same cross-subsidization the cable industry would later rely on to introduce broadband and phone service.
The cable industry feared phone companies would charge ratepayers to subsidize their entry into the television business and sought protective legislation prohibiting the same cross-subsidization the cable industry would later rely on to introduce broadband and phone service.
More recently, after the country reached “peak cable” — the year the highest number of us subscribed to cable TV, the industry recognized it was likely all downhill from there. Comcast, in particular, specialized in empty lip service gestures to improve the customer service experience. For years, it promised to do better, only to do worse. The company even attempted to shed its bad reputation by changing the brand of its products from Comcast to “XFINITY.” Customers were not fooled, but that did not stop Charter from following Comcast’s lead, introducing the “Spectrum” brand to its products and almost burying its corporate name, which it barely references these days.
 Kagan notes not following through on the customer service experience made cable companies ripe for stunning customer losses as new competitors for video service emerged. Comcast and Charter are among the biggest losers of cable TV customers, but their bad attitudes persist. Their latest ideas? Keep raising prices, rely on tricky Broadcast TV surcharges that are soaring in cost, end customer retention offers for dissatisfied video customers, and make up the difference in lost revenue by jacking up the price of broadband service, which is already nearly all-profit.
Kagan notes not following through on the customer service experience made cable companies ripe for stunning customer losses as new competitors for video service emerged. Comcast and Charter are among the biggest losers of cable TV customers, but their bad attitudes persist. Their latest ideas? Keep raising prices, rely on tricky Broadcast TV surcharges that are soaring in cost, end customer retention offers for dissatisfied video customers, and make up the difference in lost revenue by jacking up the price of broadband service, which is already nearly all-profit.
“The bottom line for any business is always focus on the customer. If they are happy, your business will remain strong and growing,” Kagan warned.
At some point, customers will get more choices for broadband service. Community owned broadband solutions have been very successful in communities that have experienced the worst abuse AT&T, Comcast, and Charter can deliver. In the future, fixed 5G wireless may provide perfectly respectable internet service if it is not data capped. Next generation satellite providers, interloping independent fiber to the home providers, and mesh wireless providers may offer consumers a number of options that can deliver suitable service and perhaps finally put cable and phone companies in their place.


 Subscribe
Subscribe “Frontier offers a level of suckage that cannot be proportionally compared with any other company in America. Stabbing yourself with knitting needles is less painful than their snail slow internet service and dealing with customer service agents that formerly served as prison guards at a Syrian detention camp.” — A deeply dissatisfied Frontier DSL customer in Ohio
“Frontier offers a level of suckage that cannot be proportionally compared with any other company in America. Stabbing yourself with knitting needles is less painful than their snail slow internet service and dealing with customer service agents that formerly served as prison guards at a Syrian detention camp.” — A deeply dissatisfied Frontier DSL customer in Ohio Frontier’s worst performance is delivered in legacy DSL service areas, where its aging copper wire network is often incapable of delivering 21st century broadband speeds. In many areas, speeds drop well below 10 Mbps during peak usage. Even worse, company officials signaled that the company
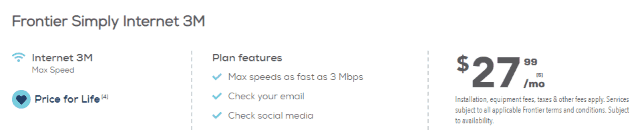
Frontier’s worst performance is delivered in legacy DSL service areas, where its aging copper wire network is often incapable of delivering 21st century broadband speeds. In many areas, speeds drop well below 10 Mbps during peak usage. Even worse, company officials signaled that the company 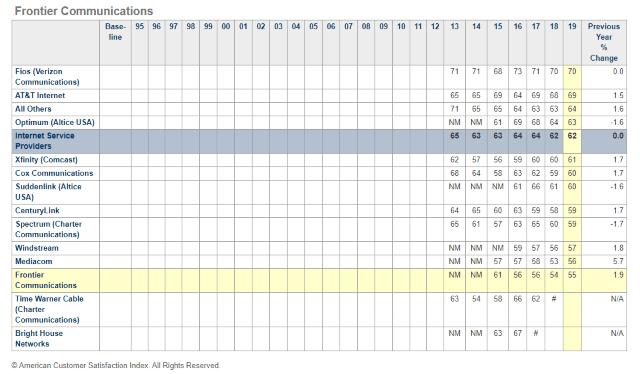
 The top 10 service providers in the United States collectively lost over 1.25 million paid television customers in the first three months of 2019, providing further evidence that cord-cutting is accelerating.
The top 10 service providers in the United States collectively lost over 1.25 million paid television customers in the first three months of 2019, providing further evidence that cord-cutting is accelerating. Mediacom Business reports the company will be increasing broadband speeds for its commercial customers around the country beginning April 1st without a change in rates.
Mediacom Business reports the company will be increasing broadband speeds for its commercial customers around the country beginning April 1st without a change in rates.