Charter Communications is petitioning the Federal Communications Commission for permission to usage cap its internet customers two years before the FCC’s ban on the company imposing data caps runs out.
Charter Communications is petitioning the Federal Communications Commission for permission to usage cap its internet customers two years before the FCC’s ban on the company imposing data caps runs out.
Charter, which does business as Spectrum, is seeking an early exit from some FCC-imposed deal conditions Charter agreed to as part of an approval of its 2016 merger with Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks. Out of concern that Charter’s merger could harm emerging online video streaming competition, the FCC required the company to not charge fees to streaming services like Netflix and Hulu to carry video traffic to its customers and not impose data caps and usage based billing schemes that would limit online video consumption for seven years.
“New Charter’s increased broadband footprint and desire to protect its video profits will increase incentives to impose data caps and usage-based prices in order to make watching online video more expensive, and in particular more expensive than subscribing to a traditional pay-TV bundle,” the FCC concluded in its 2016 order approving the merger, with conditions. “For seven years, we prohibit New Charter from imposing data caps or charging usage-based pricing for its residential broadband service. This condition ensures that New Charter will continue Charter’s past pricing practices and protects subscribers from paying fees designed to make online video consumption more expensive leading subscribers to stick with a traditional pay-TV bundle.”
Charter last week argued that with cord-cutting at an all-time high and video streaming alternative cable and video packages flourishing, there is no reason to continue the seven-year ban on data caps, noting that many other large providers including AT&T, Cox, Altice, and Comcast are free to impose data caps of their own.
“They are able to do so because, unlike Charter, they are not subject to a condition that artificially and unilaterally restricts the packages available to their customers,” Charter argues in its filing. “The online video distribution marketplace is almost unrecognizable compared to what existed in 2016. […] Consumers have never had more online video choices.”
Charter said a sunset of the prohibition of data caps was now overdue.
“As data usage skyrockets, the [ban on data caps and usage-based billing] artificially hamstrings Charter’s ability to allocate the costs of maintaining its network in a way that is efficient and fair for all of its customers—above-average, average, and light users alike,” the company argued. “Charter should be afforded the same flexibility as other broadband providers to respond to developments in the market. In short, tremendous changes in the marketplace have rendered the [ban on data caps and usage-based billing] no longer necessary, and thus ending it in 2021 would be in the public interest.”
 The FCC’s 2016 order approving the merger between Charter Communications, Time Warner Cable, and Bright House Networks, with a 7-year prohibition on data caps, was not unanimous. Separate statements from Republican Commissioners Ajit Pai and Michael O’Rielly were highly critical of most of the deal conditions the then-Democratic majority favored. Four years later, Pai now presides as chairman over a Republican-majority FCC that could take a favorable view of Charter’s request to end deal conditions early.
The FCC’s 2016 order approving the merger between Charter Communications, Time Warner Cable, and Bright House Networks, with a 7-year prohibition on data caps, was not unanimous. Separate statements from Republican Commissioners Ajit Pai and Michael O’Rielly were highly critical of most of the deal conditions the then-Democratic majority favored. Four years later, Pai now presides as chairman over a Republican-majority FCC that could take a favorable view of Charter’s request to end deal conditions early.
In 2016, Pai’s spokesperson complained about the imposition of deal conditions in the Charter-Time Warner Cable-Bright House merger, telling The Hill, “The FCC’s merger review process is badly broken. [Then FCC] Chairman Wheeler’s order isn’t about competition, competition, competition; it’s about regulation, regulation, regulation. It’s about imposing conditions that have nothing to do with the merits of this transaction. It’s about the government micromanaging the internet economy.”
Charter’s June 2020 filing focuses almost exclusively on streaming video competition to argue there is no longer any need to ban the company from imposing data caps. The FCC in 2016 concluded that data caps were a powerful anti-competitive weapon that could be used to keep streaming video competition from harming cable television packages. Charter argues that consumers now have many choices for streaming video, including cable-TV alternatives, which proves they have not engaged in anti-competitive behavior.
But Charter ignored the FCC’s other chief concern about data caps and usage billing (UBP): the lack of choice of broadband competitors.
“[…] Subscribers will continue to have no (or limited) alternative cable or fiber […] options when faced with data caps and UBP designed to deter online video consumption,” the FCC concluded.
The FCC hoped that by 2023, consumers would have more options for home broadband service, likely driving usage caps out of the marketplace.
“Seven years may also provide the high-speed […] provider market sufficient time to develop further with additional investments in fiber from established wireline […] providers, Wireless 5G technology, use of smartgrid fiber for broadband, additional overbuilding, and other potential competitors to traditional wired […] providers,” the FCC wrote. “It is our expectation that these developments will foster competition in the market to make the anticompetitive use of data caps less tenable in the future.”
Unfortunately, broadband competition remains fleeting in many parts of the United States, where only one provider offers broadband service that meets the FCC’s standard of 25 Mbps for downloads.
Ironically, Charter executives were against imposing data caps on their customers when the company was seeking approval to acquire Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks.
FCC:
“Charter in particular emphasizes its aversion to data caps, stating that instead of enforcing usage limits it chooses to market the absence of data caps as a competitive advantage. Charter also argues there is a strong business case for not implementing caps. Specifically, Charter explains that it terminated its enforcement of the usage limits trial in the AUP in January 2012 because the benefits to customers of continuing the trial (minimizing bandwidth consumption to preserve a positive Internet experience) would not exceed the program’s costs. Charter also states that caps create marketing challenges because they complicate consumer purchasing decisions. Furthermore, Charter argues that data caps increase churn among subscribers. Finally, Charter states that it plans to distinguish itself from its competitors based largely on the quality and speed of its broadband offerings and that data caps undermine that marketing message.”
 But the FCC remained unconvinced by Charter’s statements. In a review of confidential internal company documents, the FCC found multiple instances where Time Warner Cable had not completely abandoned the idea of data caps, despite multiple high-profile consumer backlashes against the idea.
But the FCC remained unconvinced by Charter’s statements. In a review of confidential internal company documents, the FCC found multiple instances where Time Warner Cable had not completely abandoned the idea of data caps, despite multiple high-profile consumer backlashes against the idea.
“We also note that despite Time Warner Cable’s relative lack of success in implementing usage-based billing, its internal documents leave no doubt that it is also incentivized to use data caps to protect its [cable TV] business,” the FCC concluded.
Four years later, Charter is among many cable operators reporting staggering losses of video customers that have chosen to “cut the cord” on cable television and have switched to a streaming competitor. If an incentive to data cap customers to protect video revenue was there in 2016, it stands to be much stronger today in 2020.
The FCC is now seeking public comment on Charter’s proposal until July 22, 2020. Stop the Cap! plans to file extensive comments on the matter and will shortly publish a guide for readers offering sample letters that can be sent to the FCC on this issue.


 Subscribe
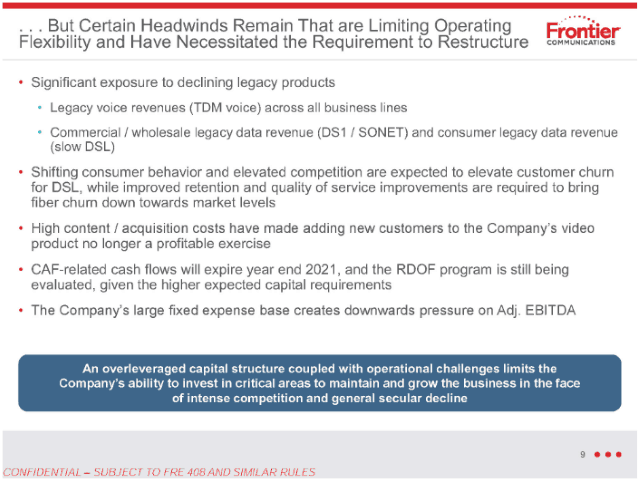
Subscribe Frontier Communications is seeking to slow or block rural broadband funding for tens of thousands of rural Americans that live inside Frontier service areas but cannot subscribe to broadband service because the company does not offer it.
Frontier Communications is seeking to slow or block rural broadband funding for tens of thousands of rural Americans that live inside Frontier service areas but cannot subscribe to broadband service because the company does not offer it. In early April, Frontier
In early April, Frontier 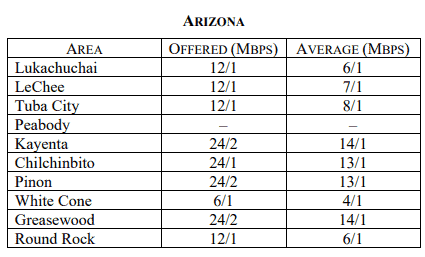


 Stankey’s predecessor, Randall Stephenson, will exit as AT&T’s CEO in July. He leaves a much larger conglomerate than what he started with. AT&T has diversified from its telephone and wireless portfolio with several major acquisitions, including DirecTV — the satellite TV service, and Time Warner (Entertainment), a Hollywood studio and entertainment giant. The result is a company loaded with debt and a revolt by activist investors that question the wisdom of creating the 2010s version of AOL-Time Warner.
Stankey’s predecessor, Randall Stephenson, will exit as AT&T’s CEO in July. He leaves a much larger conglomerate than what he started with. AT&T has diversified from its telephone and wireless portfolio with several major acquisitions, including DirecTV — the satellite TV service, and Time Warner (Entertainment), a Hollywood studio and entertainment giant. The result is a company loaded with debt and a revolt by activist investors that question the wisdom of creating the 2010s version of AOL-Time Warner.

 In reality, 5G is nothing more than an overhyped wireless technology upgrade that can either be slightly faster than existing 4G LTE networks, or considerably faster if adequate wireless spectrum is available for short distance communications. In either case, the energy emitted by traditional cell towers or small cells is infinitesimal compared to much stronger local TV and radio stations. In fact, the fastest 5G networks operate on millimeter wave frequencies that cannot penetrate walls and doors and are capable of reaching only a few blocks away at most.
In reality, 5G is nothing more than an overhyped wireless technology upgrade that can either be slightly faster than existing 4G LTE networks, or considerably faster if adequate wireless spectrum is available for short distance communications. In either case, the energy emitted by traditional cell towers or small cells is infinitesimal compared to much stronger local TV and radio stations. In fact, the fastest 5G networks operate on millimeter wave frequencies that cannot penetrate walls and doors and are capable of reaching only a few blocks away at most. Frontier Communications has revealed to investors what many probably realized long ago — the independent phone company chronically underinvested in network upgrades and repairs for years, giving customers an excuse to switch providers.
Frontier Communications has revealed to investors what many probably realized long ago — the independent phone company chronically underinvested in network upgrades and repairs for years, giving customers an excuse to switch providers.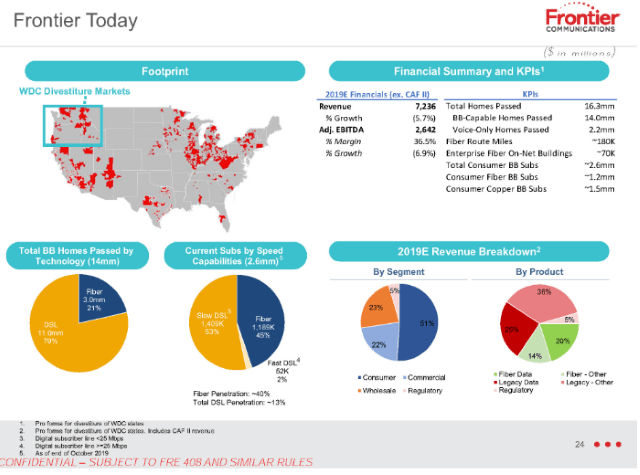

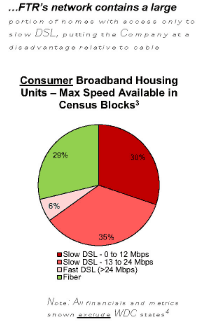 So why would a company like Frontier not immediately hit the upgrade button and start a massive copper retirement-fiber upgrade plan to keep the company in the black? In short, Frontier has survived chronic underinvestment because of a lack of broadband competition. Nearly two million Frontier customers have only one choice for internet access: Frontier. For another 11.3 million, there is only one other choice – a cable company that many detest. Frontier has enjoyed its broadband monopoly/duopoly for at least two decades. So long as its customers have fewer options, Frontier is under less pressure to invest in upgrades.
So why would a company like Frontier not immediately hit the upgrade button and start a massive copper retirement-fiber upgrade plan to keep the company in the black? In short, Frontier has survived chronic underinvestment because of a lack of broadband competition. Nearly two million Frontier customers have only one choice for internet access: Frontier. For another 11.3 million, there is only one other choice – a cable company that many detest. Frontier has enjoyed its broadband monopoly/duopoly for at least two decades. So long as its customers have fewer options, Frontier is under less pressure to invest in upgrades.