West Virginia has returned to broadband mapping the old-fashioned way, with local volunteers fanning out across various areas of the Eastern Panhandle to get a true picture of what broadband service is like on the ground.
The Region 9 Planning and Development Council is helping coordinate the project, currently surveying residents in Berkeley, Jefferson, and Morgan counties. Residents and area businesses can complete a 22-question survey online or on paper, with copies available at most area public libraries.
The Council is trying to ascertain what specific neighborhoods still lack broadband service and also asks current broadband customers to rate the performance of their current provider — like Frontier Communications or a local cable operator. GIS analyst Matthew Mullenax told the Herald-Mail the survey gives a chance for customers to express their views about the speed of their connection, how reliable the service is, and how much it costs.
The West Virginia Broadband Deployment Council is effectively running a mapping “do-over,” to replace the highly-criticized broadband map originally drawn by Connect West Virginia, a state chapter of Connected Nation, that suggested 90-95% of the state had access to broadband when it was produced over three years ago.
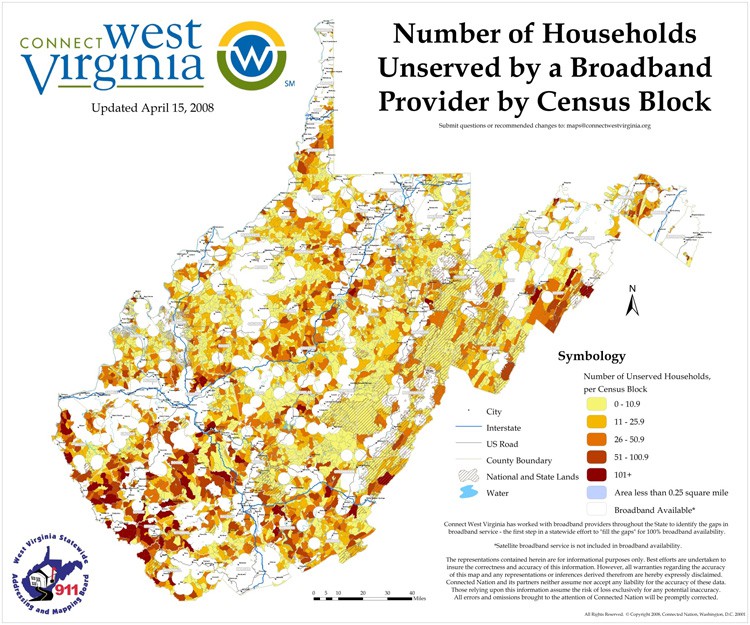
Connected Nation’s 2008 map has been criticized for being over-optimistic about broadband availability in West Virginia.
Connected Nation has direct ties to some of the nation’s largest telecommunications companies, and despite its non-profit status, heavily lobbies legislators on broadband-related issues. The group largely relies on data voluntarily supplied by providers themselves, and critics accuse the group of doing little to verify the accuracy of that data. As a result, states are left with inaccurate, over-optimistic maps that suggest broadband availability is not a problem.
Broadband mapping projects can cost taxpayers millions, paid for by federal grants earmarked for mapping projects. But in communities like Paw Paw, W.V., the costs of not having broadband are just as high for local residents who find good-paying technology jobs largely unavailable in the community, which lacks adequate broadband service.
Mullenex hopes once an accurate map can be drawn, the state can create a strategic plan to push for broadband expansion in areas where service is lacking. The Council hopes its efforts will help pinpoint the areas of greatest need, and direct federal and state grant funding to improve broadband service for affected communities.
- The West Virginia Broadband Deployment Council released this 2012 map. Areas marked in dark green have no broadband service of any kind, including wireless mobile broadband.


 Subscribe
Subscribe