 Frontier Communications is continuing to suffer service outages and problems across many of their respective service areas. Some of the most serious continue in West Virginia, especially in the northern panhandle region where emergency response agencies continue to complain about sub-standard service from the phone company that took over Verizon phone lines this past summer.
Frontier Communications is continuing to suffer service outages and problems across many of their respective service areas. Some of the most serious continue in West Virginia, especially in the northern panhandle region where emergency response agencies continue to complain about sub-standard service from the phone company that took over Verizon phone lines this past summer.
Hancock County officials report their T1 line that connects emergency dispatchers with the county’s dispatch radio system was out of service again early Wednesday evening. This Frontier-owned and maintained circuit has suffered repeated outages over the past year, and the latest outage comes after company officials promised to inspect the 12,000 foot line inch-by-inch. Once again, the county’s emergency agency is relying on help from nearby counties and a backup radio system to communicate with at least some of the area’s police and fire departments.
Outages of 911 service are not just limited to West Virginia. Illinois Valley (Oregon) Fire District Chief Harry Rich was forced to rely on amateur radio operators and extra staffing in county firehouses to cope with a 911 system failure caused by Frontier service problems in late September. Rich called a public meeting in late October with Cave Junction Mayor Don Moore, Josephine County Sheriff Gil Gilbertson and Josephine County Commissioner Dave Toler to discuss the implications of Frontier’s outage and what steps the region needs to take to mitigate future outages.
In Greencastle, Indiana a Frontier phone outage disrupted service for DePauw University and the Putnam County Hospital Oct. 20. In Meshoppen, Pennsylvania an outage caused by a downtown fire on Oct. 24 left 1,200 homes in the community without telephone service for most of the day. Frontier has also suffered periodic copper wire thefts, particularly in the Appalachian region where illicit sales of copper can bring quick cash for those addicted to drugs. In Eastern Kanawha County, West Virginia, some 100 customers lost service for at least a day after thieves yanked phone cables right off the poles.
In Minster, Ohio village officials have hired a law firm to sue Frontier Communications over a wiring dispute. Village officials accuse Frontier of being intransigent over the removal of telephone lines from poles to bury them underground. Village Solicitor Jim Hearn told the local newspaper utility companies should be responsible for the costs of installing underground wiring.
In Wenatchee, a community in north-central Washington state, Frontier’s general manager is going all out to try and assuage customers Frontier will provide better service than Verizon. Steve Sandman went as far as to hand out his direct number to the local media, inviting residents with service problems to call. It’s (509) 662-9242.
Sandman promises other changes for his customers, according to The Wenatchee World:
Sandman said all Frontier technicians will be fully trained in the installation of phones, internet and TV. No more modems sent through the mail for the customer to install by themselves, he said.
“We’ll be there on the premises for complete installation,” he said. “And, if the customer needs it, we’ll provide some fundamental training on how to turn on the computer, hook up to the internet and get started using online services. Or give advice on how to use the TV remote.”
But all of these issues pale in comparison to the all-out battle forming in the state of West Virginia over broadband stimulus money awarded to help Frontier extend fiber broadband service to local government and community institutions. One of their biggest competitors, Citynet, has launched a well-coordinated attack on what it calls “a flawed plan that does nothing to provide faster Internet speeds or lower the majority of Internet costs for West Virginians.”
 Frontier will spend $40 million of federal broadband stimulus money on a network that will deliver fiber-fast speeds only to government, educational, and health care institutions.
Frontier will spend $40 million of federal broadband stimulus money on a network that will deliver fiber-fast speeds only to government, educational, and health care institutions.
James Martin II, president and CEO of Citynet argues Frontier is building a state of the art fiber network very few West Virginians will ever get to use, from which it will profit handsomely delivering service to government entities with which it already has contracts. For the rest of West Virginian homes and businesses, Frontier will deliver outdated DSL service delivering an average of 3Mbps service at a time when adjacent states are enjoying service 2-4 times faster.
Citynet argues funding would be better spent on a middle mile, open fiber backbone available for use by all-comers. Martin notes West Virginia is one of the few states in the northeast and mid-Atlantic region almost completely bypassed by the core Internet backbone. The only exception is a fiber link connecting Pittsburgh with Columbus, Ohio, which briefly traverses the northern panhandle of West Virginia. Citynet’s perspective is that West Virginia cannot improve its poor broadband standing — 48th in the nation, unless it has appropriate infrastructure to tap into for service.
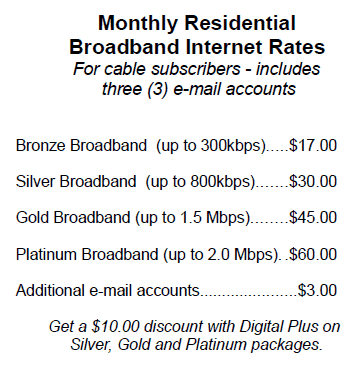
As an example, Martin points to the community of Philippi, served by fiber to the home cable TV and broadband service. The community’s fiber network is capable of Lamborghini speeds between homes within Philippi. But the community can only afford a single 45 megabit DS-3 connection to the outside world, provided by Citynet for just under $8,000 a month. That line is shared among every broadband customer in Philippi trying to get out onto the Internet. The result is that Philippi residents can only buy a broadband account with speeds up to 2Mbps for $60 a month on that all-fiber network. That’s equivalent to being forced to drive that Lamborghini on a dirt road.
Martin says if the broadband stimulus money was spent on constructing a statewide open fiber backbone, they could sell the community a 1Gbps pipeline for around $3,000 a month.
Philippi's fiber optic broadband is not so fast, thanks to a bottleneck between the community and the rest of the Internet
“West Virginia is at a crossroads,” Martin said in a prepared statement. “We can build a ‘middle-mile’ solution for high-speed Internet infrastructure and create jobs, or we can stick with the status quo and watch West Virginia fall behind once again. The outcome will determine our state’s economic growth for years to come.”
The state, according to Martin, is reneging on its promise to build a broadband network that will deliver improved service to institutional users as well as at least 700,000 homes and 110,000 business in the state.
Instead, the project would only serve 1,000 “points of interest,” he said. The state’s plan would limit Internet speeds and make broadband service unaffordable, Martin argues.
“If the state were to build a true middle-mile solution, then businesses and residential Internet customers would see a significant reduction in price, as well as an increase in quality, capacity and speed,” Martin said. “Regretfully, the state chose to support a plan that relies on outdated telephone lines and a monopoly.”
Of course, Citynet does have a vested interest in the outcome of the project. As a provider specializing in selling bulk broadband lines, they would be a prime beneficiary of a government-backed middle-mile broadband network. Citynet’s argument that funding should be spent primarily on that network ignores the reality few new entrants are likely to enter West Virginia’s rural broadband market, with or without the benefit of a robust broadband backbone. One of the biggest flaws of broadband stimulus spending is that much of the money will never directly provide “last mile” access to individual consumers and businesses that want broadband service where none is available.
Citynet needs to acknowledge much of West Virginia’s broadband is going to come from the phone company or a local municipality that elects to build its own network. While cable companies deliver service in larger cities and suburban areas, large swaths of the state will never be wired for cable. In fact, West Virginia is poorly covered even by wireless companies who see little benefit building extensive cell tower networks in the notoriously mountainous areas of the state that serve few residents. The only existing rural telecommunications infrastructure universally available is copper telephone wires. Like it or not, Frontier Communications will be the biggest provider of broadband in rural West Virginia. A fiber backbone network alone delivers minor benefits to those residents who either cannot connect at any broadband speed, or are stuck with Frontier’s current 1-3Mbps DSL service.
Still, Citynet’s campaign is a useful reminder that too many broadband stimulus projects direct most of their money to networks ordinary consumers and businesses will never access. And so long as local governments, schools, and hospitals “get theirs,” they have little interest in fighting to share those networks with consumers and for-profit businesses.
Citynet produced two radio ads criticizing West Virginia’s allocation of broadband stimulus money, and Jim Martin appeared on a local radio show to explain to West Virginia why this issue matters. (Ads from 11/2010 — Interview with Jim Martin: September 16, 2010) (18 minutes)
You must remain on this page to hear the clip, or you can download the clip and listen later.
<
p style=”text-align: center;”>
Ultimately, Verizon may get the last word, even after they abandoned the state’s landline customers. Charleston, the state capital, has been selected as one of the early communities to receive Verizon Wireless’ new 4G LTE wireless broadband network, according to WTRF-TV:
Verizon subscribers in Charleston with devices that are 4G compatible will see changes within the next six to seven weeks. The whole city is expected to be covered by the network by mid-2011, according to company officials. From there, it will be expanded to cover Huntington, Parkersburg, Wheeling, Weirton, Beckley, Clarksburg, Morgantown, Fairmont and Martinsburg by 2013.
The company also plans to expand coverage along the entire Interstate 79 corridor from Charleston to Clarksburg.
The decision to include Charleston among the 39 metropolitan areas where Verizon would deploy its 4G network left many analysts of the industry scratching their heads, although they noted in online posts that Rockefeller chairs the Senate committee that regulates the telecommunications industry.
Should West Virginians find Verizon Wireless a suitable replacement for their landlines, Frontier may have bought themselves a pig in the poke.
[flv width=”640″ height=”500″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/West Virginia Frontier 11-4-10.flv[/flv]
WTOV-TV covers the emergency services outage in northwestern West Virginia in two reports, WBOY-TV covers the Citynet-Frontier controversy, and WTRF-TV covers the arrival of Verizon’s LTE upgrade, starting with Charleston. (7 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe

