In Kyle McSlarrow’s world, the only broadband problem is the one invented by the Federal Communications Commission when it claims that service is not being deployed to all Americans on a “reasonable and timely” basis. The head of the National Cable and Telecommunications Association (NCTA), the cable industry’s lobbying group, has declared today’s broadband a U.S. “success story that keeps getting better.”
Writing in the group’s “CableTechTalk” blog, McSlarrow tells his readers that 95 percent of Americans already have broadband service available to them that meets the 4Mbps minimum speed standard proposed by the FCC, so where is the big problem?
McSlarrow’s interest in the economics of rural broadband is ironic considering the cable industry routinely bypasses rural Americans. Where cable lines do predominate, meeting the FCC’s anemic 4Mbps minimum speed standard is not the biggest problem — cost is. Where cable lines don’t reach, speed is an issue for many wireless and DSL subscribers. For others, broadband service is not available at any price.
McSlarrow plays cable’s advantage on speed issues to promote minimum speeds higher than those sought by phone companies like AT&T and Verizon. Of course, cable broadband does not rely on antiquated copper wire telephone networks. In rural areas, many of these networks are held together with minimal investment. DSL at any speed can be a luxury when available.
McSlarrow’s recognition that most of rural America will continue to be served by telephone companies doesn’t stop the cable industry from seeking an advantage over their nearest competitors by advocating for reduced subsidies for rural areas and policies that guarantee no potential competitor can ever see a dime in government broadband money.
Because the report plainly acknowledges that there is no reasonable business case to be made for extending broadband facilities to many of the unserved homes. So instead of viewing the report’s finding as an indictment of broadband providers, it’s perhaps better read as a statement of principle by the Chairman and two commissioners that, in their opinion, broadband already should be universally available, and, if there is no business case for that universal deployment, the government may have to step in to achieve it. So far as that goes, we agree. For example, we support the report’s call to action on specific items that will speed broadband deployment to unserved communities. Immediate FCC action on Universal Service Fund (USF) reform and pole attachment policy is critical to connecting unserved areas.
As explained in comments we filed last week, our industry strongly supports the USF reforms recommended in the National Broadband Plan (NBP). To fund the FCC’s broadband USF proposals, we recommend adopting our proposal – filed in a November 2009 rulemaking petition – to reduce subsidies in rural areas where ample phone competition exists. The sooner the Commission reduces unnecessary funding in the existing high-cost support program, the sooner it can direct funding to broadband deployment and adoption.
McSlarrow’s comments neglect to tell the whole story about what the NCTA actually wrote in its comments filed with the FCC:
The 4Mbps/1Mbps standard reflects today’s marketplace reality that most consumers choose not to purchase the highest speed tiers that are offered by their broadband provider. By setting a standard based on the services actually purchased by consumers, the Plan strikes the appropriate balance – not so low that it deprives consumers of the ability to purchase a service that meets their needs and not so high that it will require a significant infusion of new government funding.
Second, based on this definition of broadband, the Plan found that the vast majority of Americans – 95% of households – already have access to broadband, and that 80% of those consumers live in geographic areas served by two or more providers. For these areas where broadband has already been deployed, there is no basis for any increase in support; indeed, as NCTA has demonstrated, in many of these areas there is no basis for any high-cost support at all.
Consequently, the only areas that should see an increase in the support they receive are those areas that do not have broadband and qualify for CAF support, i.e., areas where there currently is no business case for private investment in broadband facilities.

In Great Britain, speeds promised don't match speeds delivered. The FCC is studying whether the same is true in the United States.
McSlarrow is disingenuous about Americans’ interest in improved broadband. It’s not surprising many do not choose the highest speed tiers available from telephone and cable providers when one considers the premium prices charged for that service. Some NCTA members charge $99 for 50/5Mbps service, which in other countries like Hong Kong sells for a fraction of that price. One need only consider Google’s plan to deliver 1Gbps service to a handful of American communities. It’s easier to count the communities that were not interested in this super-fast service.
The cable industry can afford to relent on a 4Mbps minimum speed standard for downloading as virtually all cable broadband providers already offer “standard service” plans well above that rate. The cable industry’s own “lite” plans, usually 1.5Mbps or less, are not exactly the industry’s most popular. Americans will choose higher speed service at the right price.
Broadband availability figures have become an important political issue, which is why controlling broadband mapping is so important to cable and phone companies. Being able to offer that “95 percent of Americans already have access,” a figure in dispute by the way, can make a big difference in the debate. As Stop the Cap! readers have seen repeatedly, broadband maps that depict broadband service as widely available in many areas actually is not, especially from phone company DSL service, which depends heavily on the quality of the existing infrastructure.
Most importantly, the NCTA seeks a new, even stricter standard for broadband funding under Universal Service Fund reform that would immediately deny money to any applicant that cannot prove there is no chance for any private investment in broadband. As we’ve seen from broadband improvement applications filed under the Obama Administration’s broadband stimulus program, cable and phone companies routinely object to most proposals, claiming “duplication” of existing broadband service even in areas they have chosen not to provide service. The NCTA would have us set the bar even lower, allowing any private entity to kill funding projects based solely on their claimed interest in providing the service themselves.
One sensitive spot the FCC did manage to hit was taking providers to task for advertising broadband speeds they don’t actually provide to customers. While DSL speeds vary based on distance from the telephone company’s central office, cable broadband speeds vary depending on how many customers are online at any particular moment. The cable industry’s shared access platform can create major bottlenecks in high-use neighborhoods, dramatically reducing speeds for every customer. While some cable operators are better than others at re-dividing neighborhoods to increase capacity, others won’t spend the money to upgrade an area until service becomes intolerable. That means consumers sold 10Mbps service may actually find it running at less than half that during evening hours.
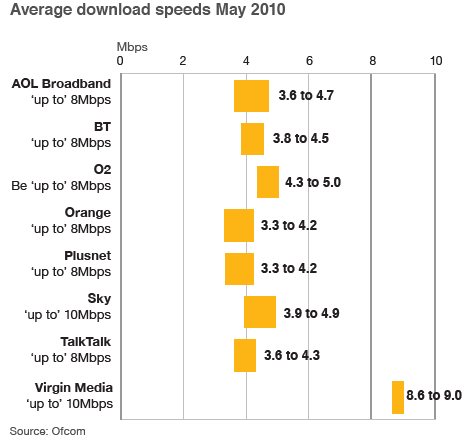
A sampling of British cable and telephone company DSL providers, all of which aren't giving their customers what they are paying for.
McSlarrow’s view is there isn’t a problem there either — the FCC is relying on old data:
The key statistics in the report are drawn from Form 477 data for December 2008, data that was out of date when it was released earlier this year and is now 18 months old. Broadband providers have made two subsequent Form 477 filings (with another one scheduled in a few weeks), so the reliance on stale data is frustrating.
Equally troubling is the Commission’s repetition of the NBP’s claim that “actual” broadband speeds are only half of “advertised” speeds. After the NBP was released, we submitted an expert technical report demonstrating that the comScore data used was deeply flawed. Since then, cable and telco ISPs have been working constructively with Commission staff on a hardware-based testing regime that should produce more accurate results. Given the hard work that has been devoted to produce accurate speed measurements, it is disheartening that the 706 Report chose to perpetuate the NBP’s flawed speed data conclusions.
Finally, some of the data relied on in the 706 Report is not publicly available. The report relies extensively on a cost model created for the NBP, but that model hasn’t been released, making it impossible to validate its results. The Commission also repeatedly refers to an FCC staff report on international trends, but that report also has not been released.
The frustration McSlarrow writes about is shared by cable subscribers stuck in overloaded neighborhoods where service does not come close to marketed speeds. The FCC is conducting an independent speed analysis that goes beyond speedtest data, and the results will be forthcoming. In other countries where similar speed claims have not met reality, providers were usually found culpable for promising service they didn’t deliver.
Just ask Ofcom, the British regulatory agency charged with addressing this dilemma. Earlier today they released evidence that 97 percent of UK broadband customers were not actually getting the speeds they were promised, and the gap between marketed speed and actual speed was growing. Will things be any different for American providers who use fine print to disclaim their bold marketing promises about speed? Time will tell.
Finally, McSlarrow’s concerns about withheld data is ironic enough to call it a “pot to kettle” moment. As those challenged with broadband mapping can attest, nobody keeps raw data about broadband availability and speeds closer to the vest than cable and telephone companies.
Of course, the ultimate agenda of the NCTA is to defend its industry’s record in broadband service, which means reducing any broadband challenges into little more than whining by Americans who don’t know how good they have it.


 Subscribe
Subscribe

I had the same issue on my 4Mbit cable during evenings, I was lucky to get 1-2Mbit speed until several hours later.
After I cancelled my TV/Phone over a cost increase, I went with the dedicated 8Mbit plan, even that only runs about 5Mbit at peak hours.
I’d very much believe the results in the US to mirror those of the UK. I think these plans should be advertised as actual average peak speeds when customers are actually trying to use them, not off-peak.